Plastics are an inseparable part of modern human life, with nearly one million tons produced globally every day. As is well known, it takes hundreds of years for plastics to decompose in nature. Therefore, it is essential to handle them responsibly after their initial use. Recycling plays a vital role in extending the life cycle of these materials and preventing the environmental consequences of their disposal in nature. Without recycling, plastics typically end up in landfills where they remain undecomposed, are incinerated for energy—causing air pollution—or break down into harmful microplastics that contaminate the environment.
Plastic recycling is a complex process influenced by markets, policies, and regional regulations. Effective recycling requires cooperation at all stages of the plastic product’s lifecycle. Everyone, including designers, manufacturers, consumers, and waste collectors, plays a crucial role in ensuring high-quality recycling of plastic waste.
The Impact of Global Markets on Plastic Production and Recycling:
Demand for Recycled Materials:
Markets and demand for recycled materials directly influence the economic viability of recycling. High demand for recycled plastics can make recycling more profitable and encourage investment in recycling infrastructure. But when market demand is low, recycling operations may become financially unsustainable, discouraging businesses and municipalities from continuing or expanding recycling efforts.
Raw Material Prices:
The cost of raw materials—such as petrochemical products and polymer compounds—can significantly impact recycling processes. When raw material prices are low, producing new plastic may become cheaper than recycling, leading to a decline in recycling rates. This poses a challenge for recycling industries, which are heavily dependent on global markets and price fluctuations.
Global Market Influence:
Many developed countries export their plastic and other recyclable materials to developing nations. When these international markets become restricted or new regulations are enforced, the entire recycling process can be disrupted or slowed down.

Employment Impact:
Recycling processes create job opportunities that are socially valuable for communities. These opportunities span a wide range—from collection and sorting of recyclable materials to the manufacturing of products made from recycled content. Government policies and regulations can play a key role in supporting and expanding these employment opportunities.
Why Is Plastic Recycling So Important?
If efforts to recycle plastic materials are not significantly increased, by 2050 the amount of plastic in the oceans may surpass the number of fish. Additionally, the production of virgin plastic could account for up to 15% of global greenhouse gas emissions. These projections highlight the urgent need for immediate action.
Persian Sanat Company, as a manufacturer of plastic products, is committed to recycling damaged pallets and pallet boxes returned by its customers, preventing them from becoming plastic waste. Utilizing advanced equipment and modern recycling technologies, we process products that have reached the end of their life cycle. Given the importance of product durability and quality, the separation and sorting of different types of plastics is a critical step in the recycling process.
The recycling systems used at Persian Sanat include shredders and granulators, which we briefly describe below:

Grinding
Grinding is the process in which plastic materials are broken down into smaller pieces. This process is particularly important in the plastic recycling industry, where it is used to convert plastic waste into reusable material.
Grinding Process:
Material Collection:
The first stage of the grinding process involves collecting used plastic materials. These may include damaged and decommissioned products, plastic bottles, bags, boxes, and various types of broken or unusable pallets and pallet boxes.
Washing:
Before grinding, plastic materials must be thoroughly washed to remove any dirt, oil, or contaminants. This step improves the quality of the recycled material.
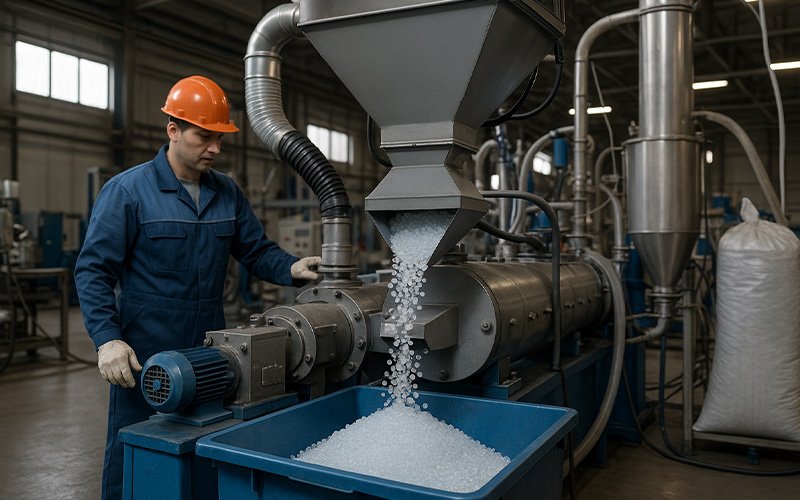
Grinding:
After washing, the plastic is fed into a grinding machine. In this stage, the material is subjected to pressure and cutting forces, breaking it down into smaller pieces or flakes. Grinding prepares the plastic for further recycling steps, such as granulation. There are different types of grinding machines, chosen based on the type of material and the required output size.
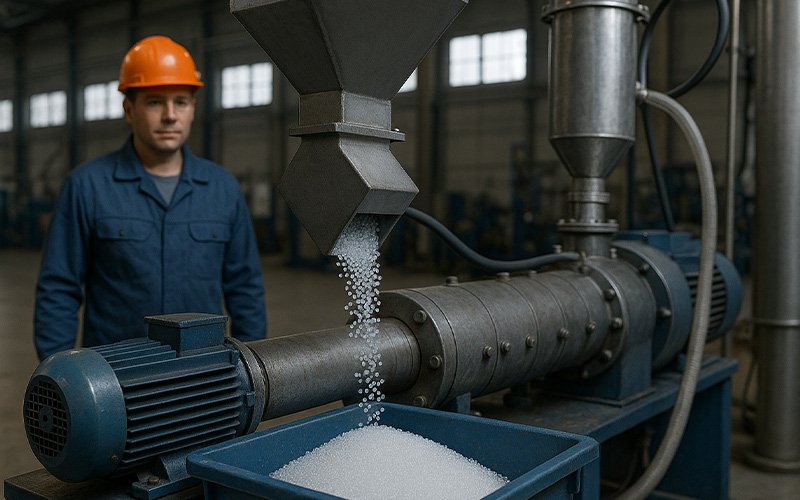

Types of Grinders:
Hammer Mill Grinder: As the name suggests, these grinders use rotating hammers to strike and crush the material into smaller fragments.
Blade Grinder (Granulator Type):In this type of machine, the plastic is placed into a special chamber and shredded using sharp, high-speed blades—similar to the function of a meat grinder or electric food chopper.
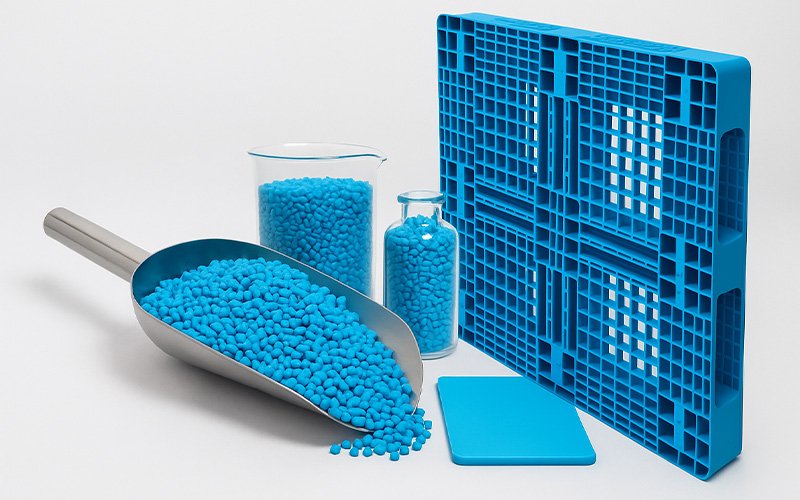
Granules
Granulation is the process of converting shredded plastic materials into small granules that can be reused in the production of new plastic products. These granules are small, uniform plastic pellets that serve as raw material for manufacturing various plastic components.
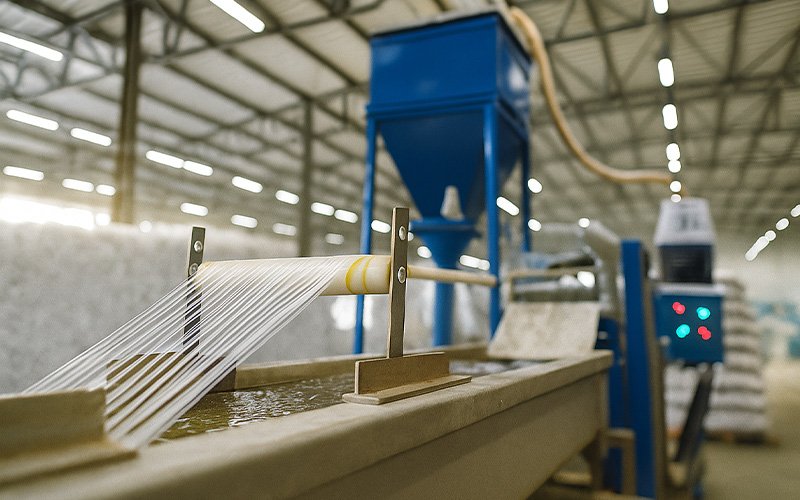

Granulation Process:
In the granulation process, the shredded plastic is first fed into a granulator machine. Inside the machine, the material is heated until it melts. The molten plastic is then pushed through a die with fine holes, forming long plastic strands. These strands are subsequently cut into smaller pieces, known as plastic granules. The size of the granules may vary, but they typically conform to standardized dimensions suitable for manufacturing processes such as injection molding, extrusion, and more. The shredding and granulation processes are especially important in the plastic recycling industry, as they enable the effective reuse of plastic waste for the production of new plastic products.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Quality and Appeal:
Recycled plastic must be durable, high-quality, and visually appealing. Proper sorting and separation of different types of plastics play a critical role in achieving this standard.
Cost and Market Conditions:
Virgin plastic is often more expensive than recycled plastic. This price advantage gives recycled plastics a competitive edge, making them more attractive in buying and selling markets.
Modern Infrastructure:
To meet future demand cost-effectively, the development of advanced, automated recycling facilities is essential.
Given the limited natural resources on Earth and the need to preserve them for future generations, prioritizing the recycling process can transform plastic recovery into a system that benefits both the environment and industry—turning today’s challenges into opportunities for a cleaner, more sustainable world.
With over half a century of experience in plastic manufacturing, Persian Sanat has consistently strived to contribute to environmental preservation through the recycling of plastic products.
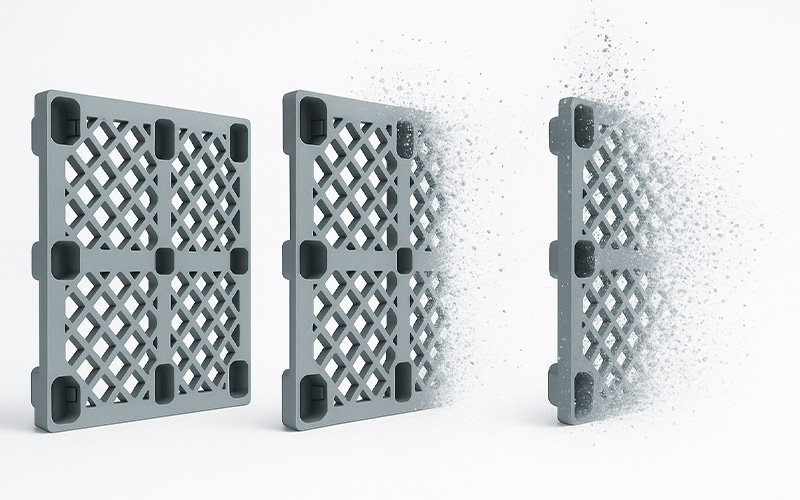
As a producer of plastic components, we believe in the future of plastics. By committing to the recycling of damaged products, we ensure that this valuable material does not end up as non-degradable waste in nature.
Plastic plays an essential and undeniable role in our daily lives, but it must be properly managed after its initial use. As we know, recycling significantly extends the useful life of plastic materials. Without recycling, plastic typically ends up in landfills, is incinerated for energy—causing air pollution—or enters the environment as harmful microplastics.
Plastic recycling is a complex process, shaped by market dynamics, policies, and local regulations. Achieving effective recycling requires collaboration across every stage of a plastic product’s lifecycle. Everyone—including designers, manufacturers, consumers, and waste collectors—has a vital role to play in enabling high-quality recycling.



